ER Diagrams
Explanation of ER Diagrams and their Importance
ER (Entity-Relationship) diagrams are a visual representation of the relationships between entities (tables) in a database. They are an important tool for designing and managing databases, as they provide a clear and concise way to understand how different tables are related to each other.
ER diagrams are used to model and plan database structures, to optimize data retrieval and to make queries more efficient. They are also used to help non-technical stakeholders understand the relationships between data tables, as they provide a simple and visual way to communicate complex data structures.
Overview of How to Use ER Diagrams to Visualize Data
ER diagrams consist of entities (tables) and relationships (connections between tables), and are created using a set of symbols and rules. Entities are represented as rectangles, and relationships are represented as lines connecting the entities.
Here's an example of an ER diagram for our employees database:
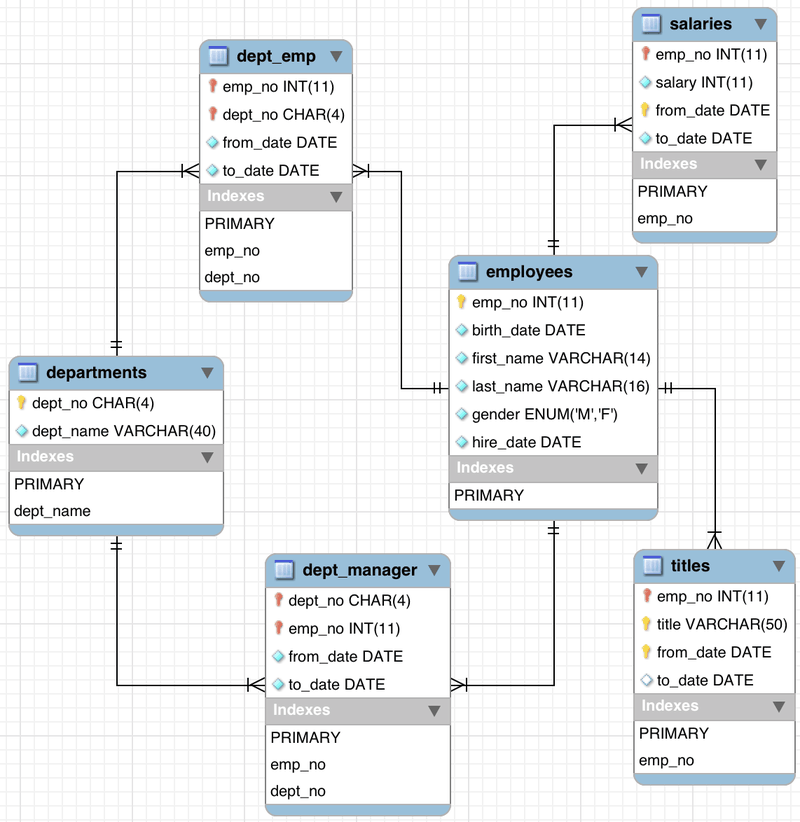
You can see the full documentation of the database on the official page here
In this diagram, the rectangles represent entities (tables), and the lines connecting the entities represent relationships between them. The relationships are labeled with the type of relationship (e.g. "belongs to", "manages", etc.), and with cardinality symbols that indicate the minimum and maximum number of instances of one entity that can be related to instances of the other entity.
ER diagrams can be used to model complex relationships between tables, including one-to-one, one-to-many, and many-to-many relationships. They can also be used to represent subtypes and supertypes, and to define constraints and business rules that govern the relationships between entities.
By using ER diagrams to visualize data, you can better understand the structure of your database and optimize your queries for maximum efficiency. ER diagrams can also be used to communicate complex data structures to non-technical stakeholders, helping to ensure that everyone involved in your data analysis projects has a common understanding of the data structures and relationships at play.
In-depth Look at How to Design an ER Diagram
The process of designing an ER (Entity-Relationship) diagram involves identifying the entities (tables) that will be included in the database, and determining the relationships between them. This process is crucial for building a database that is efficient, accurate, and easy to work with.
Here are the steps involved in designing an ER diagram:
- Identify the entities: Start by identifying the different entities (tables) that will be included in the database. These might include things like customers, products, orders, and so on.
- Determine the attributes: For each entity, determine the attributes (columns) that will be included in the table. These might include things like names, addresses, dates, and so on.
- Determine the relationships: Once you have identified the entities and their attributes, determine the relationships between them. For example, a customer might place many orders, or an order might contain many products.
- Choose the cardinality: For each relationship, determine the cardinality, or how many instances of one entity can be related to instances of another entity. This might be one-to-one, one-to-many, or many-to-many.
- Choose the modality: For each relationship, determine the modality, or whether the relationship is mandatory or optional. This might be represented using symbols such as "1" for mandatory or "0" for optional.
- Create the ER diagram: Finally, create the ER diagram using symbols and conventions that represent the entities, attributes, and relationships. These might include rectangles for entities, diamonds for relationships, and lines connecting them.
Explanation of Different Entities, Attributes, and Relationships
In ER diagrams, entities are represented as rectangles, attributes are represented as ovals, and relationships are represented as diamonds. Here's a brief explanation of each:
- Entities: Entities represent tables in the database. Each entity has a name and a set of attributes that define the data it contains.
- Attributes: Attributes represent the columns within an entity. They define the specific data that the entity contains, such as names, addresses, and dates.
- Relationships: Relationships represent the connections between entities. They define how different entities are related to each other, and the cardinality and modality of the relationship.
Some common types of relationships that you might encounter in ER diagrams include:
- One-to-one: One instance of an entity is related to only one instance of another entity.
- One-to-many: One instance of an entity is related to multiple instances of another entity.
- Many-to-many: Multiple instances of an entity are related to multiple instances of another entity.
By understanding the different entities, attributes, and relationships involved in an ER diagram, you can design a database that is efficient, accurate, and easy to work with. This can help you to analyze and manage your data more effectively, and to gain deeper insights into the patterns and trends in your data.
Explanation of How to Convert ER Diagrams to Database Schemas
Once you have designed an ER (Entity-Relationship) diagram for your database, the next step is to convert it into a database schema. This involves creating tables and relationships that reflect the structure and relationships defined in the ER diagram.
Here are the steps involved in converting an ER diagram to a database schema:
- Identify the tables: Start by identifying the tables that will be created based on the entities in the ER diagram. For example, if the ER diagram has an entity called "Employees", create a table called "Employees" in the database.
- Create the columns: For each table, create the columns that reflect the attributes of the entity in the ER diagram. For example, if the "Employees" entity has attributes such as "Employee Number", "First Name", and "Last Name", create columns in the "Employees" table with these same names and data types.
- Define the relationships: Once the tables and columns are created, define the relationships between the tables based on the relationships in the ER diagram. For example, if the "Employees" entity is related to the "Departments" entity in the ER diagram, create a foreign key column in the "Employees" table that references the primary key column in the "Departments" table.
- Specify the constraints: Finally, specify any constraints or rules that are defined in the ER diagram, such as unique constraints or not-null constraints.
- Overview of How to Create Tables and Relationships Based on the ER Diagram
Example of how to convert the ER diagram for the Employees database into a database schema:
- Identify the tables: Based on the ER diagram, we need to create tables for employees, departments, titles, salaries, and more.
- Create the columns: For the "Employees" table, we need to create columns such as "emp_no", "birth_date", "first_name", "last_name", "gender", and "hire_date". For the "Departments" table, we need to create columns such as "dept_no" and "dept_name". For the other tables, we would create columns based on the attributes defined in the ER diagram.
- Define the relationships: Based on the ER diagram, we know that employees are related to departments, titles, and salaries. To define these relationships, we would create foreign key columns in the "Employees" table that reference the primary key columns in the other tables. For example, the "Employees" table would have a foreign key column called "dept_no" that references the "dept_no" column in the "Departments" table.
- Specify the constraints: We would specify any constraints or rules that are defined in the ER diagram, such as unique constraints or not-null constraints. For example, we might specify that the "emp_no" column in the "Employees" table must be unique and not-null.
By converting the ER diagram to a database schema in this way, we can create a database that accurately reflects the structure and relationships defined in the ER diagram. This can help us to manage and analyze data more effectively, and to gain deeper insights into the patterns and trends in our data.
Wrap-up
Let's summarize what we've learn about ER diagrams :
- ER diagrams, or Entity-Relationship diagrams, are visual representations of data models that show the relationships between different entities, such as tables in a database.
- ER diagrams help to simplify complex data structures and make them easier to understand by providing a high-level view of the data and its relationships.
- ER diagrams can help companies to design more effective databases by providing a clear picture of how data is structured and related, and can help to identify areas for optimization or improvement.
- ER diagrams are important in the development process of software and databases, as they provide a blueprint for developers to follow when building and maintaining data systems.
- ER diagrams can be used to facilitate communication between stakeholders, such as developers, designers, project managers, and business users, by providing a common language and visual reference point for discussing the data model.
- By using ER diagrams to design and maintain their data models, companies can improve the accuracy, efficiency, and reliability of their data systems, which in turn can lead to better decision-making, cost savings, and increased competitiveness in the marketplace.