What are NoSQL databases?
NoSQL databases, also known as "non-relational" databases, are a class of databases that don't use the traditional relational data model. Instead, they use various data models such as document-based, key-value, column-family, or graph-based to store and manage data.
The term NoSQL was coined in the late 2000s to refer to databases that were not based on SQL, the traditional relational database query language. NoSQL databases are designed to handle large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data that cannot be easily organized into tables with predefined columns and relationships.
Key characteristics of NoSQL databases
NoSQL databases are important in modern data-driven applications because they offer several advantages over traditional relational databases. For example:
- Schema flexibility: Unlike traditional relational databases, NoSQL databases offer schema flexibility, which means that they don't enforce a predefined schema for data storage. This allows for greater flexibility in data modeling and can simplify development processes, as it eliminates the need to define and maintain rigid schemas.
- Scalability: NoSQL databases are designed to scale horizontally, which means that they can handle large volumes of data by adding more servers to the cluster. This allows for better performance and can reduce infrastructure costs over time.
- High availability: NoSQL databases are designed to offer high availability, which means that they are able to maintain a high level of uptime even in the event of hardware failures or network outages. This is achieved through techniques such as replication and sharding.
- Data model diversity: NoSQL databases offer a variety of data models, such as document-based, key-value, column-family, and graph-based, which can be used to store different types of data. This allows developers to choose the most appropriate data model for their application, rather than being limited to a single relational data model.
- Performance: NoSQL databases can offer better performance than traditional relational databases, particularly when dealing with large data sets. This is because NoSQL databases are designed to optimize read and write operations for large-scale data processing.
NoSQL databases have become increasingly popular in recent years, particularly in the context of big data and real-time data processing. They are used by a wide range of organizations, from startups to large enterprises, for applications such as e-commerce, social media, and mobile apps.
Examples of NoSQL databases
There is a lot of popular technologies of NoSQL databases such as :
- MongoDB: MongoDB is a document-based NoSQL database that uses JSON-like documents to store data. It offers scalability, flexibility, and high availability, and is often used for applications that require real-time analytics, content management, and social media. MongoDB is also known for its support for complex queries, indexing, and sharding.
- Elasticsearch: Elasticsearch is a document-based NoSQL database that is designed for full-text search and analytics. It offers fast search and retrieval of unstructured data, and is often used for applications that require real-time search, logging, and data analysis. Elasticsearch is also known for its support for indexing, sharding, and clustering.
- Redis: Redis is a key-value NoSQL database that uses in-memory data structures to store data. It offers high performance and scalability, and is often used for applications that require real-time data processing, caching, and message brokering. Redis is also known for its support for data types such as strings, hashes, lists, and sets.
- Neo4j: Neo4j is a graph-based NoSQL database that uses nodes and edges to store data. It offers high scalability and performance, and is often used for applications that require complex data modeling, such as social networking, recommendation engines, and fraud detection.
Here's quick tips on how to choose between NoSQL databases technology based on the examples given:
- MongoDB: If you require a document-based data model and need to store JSON-like data, MongoDB may be a good fit. MongoDB is also a good choice for applications that require scalability, flexibility, and high availability, such as real-time analytics, content management, and social media.
- Redis: If you require fast data processing and caching, Redis may be a good fit. Redis is optimized for in-memory data storage and retrieval, and is often used for applications that require real-time data processing, message brokering, and caching.
- Neo4j: If you require complex data modeling and relationships, such as graph-based data, Neo4j may be a good fit. Neo4j is optimized for graph-based data storage and retrieval, and is often used for applications that require social networking, recommendation engines, and fraud detection.
- Elasticsearch: If you require fast search and retrieval of unstructured data, Elasticsearch may be a good fit. Elasticsearch is specifically designed for full-text search and analytics, and is often used for applications that require real-time search, logging, and data analysis.
When choosing a NoSQL database technology, it's important to consider factors such as data model, scalability, performance, data consistency, and ease of use. It's also important to consider the specific use case and requirements of the application to determine which NoSQL technology is the best fit.
Types of NoSQL databases
NoSQL databases are a type of non-relational databases that are designed to handle large volumes of unstructured data. Unlike traditional relational databases, NoSQL databases do not rely on a fixed schema to store data, which makes them highly flexible and scalable.
There are several types of NoSQL databases, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. In this tutorial, we will provide an overview of the most common types of NoSQL databases, including document-based, key-value, column-family, and graph-based databases.
Document-Based Databases
Document-based databases store data in a semi-structured format, such as JSON or XML. Each document in the database contains a set of key-value pairs that define its structure. Document-based databases are highly flexible and can easily accommodate changes to the data schema.
One of the most popular document-based databases is MongoDB. MongoDB is known for its scalability, flexibility, and high availability. It is often used for real-time analytics, content management, and social media.
Key-Value Databases
Key-value databases store data as a collection of key-value pairs. Each key is unique and corresponds to a value, which can be a string, number, or more complex data structure. Key-value databases are highly efficient for read and write operations, making them ideal for applications that require high performance and scalability.
One of the most popular key-value databases is Redis. Redis is known for its fast in-memory data storage and retrieval, and is often used for real-time data processing, caching, and message brokering.
Column-Family Databases
Column-family databases store data in column families, which are groups of related columns. Each column can contain multiple values, which are stored as a collection of key-value pairs. Column-family databases are highly scalable and can handle large volumes of data.
One of the most popular column-family databases is Apache Cassandra. Cassandra is known for its scalability and high availability, and is often used for online transaction processing, financial services, and e-commerce.
Graph-Based Databases
Graph-based databases store data in nodes and edges, which represent entities and relationships between entities, respectively. Graph-based databases are highly flexible and can accommodate complex data models and relationships.
One of the most popular graph-based databases is Neo4j. Neo4j is known for its performance and scalability, and is often used for applications that require complex data modeling, such as social networking, recommendation engines, and fraud detection.
NoSQL databases offer several advantages over traditional relational databases, including flexibility, scalability, and performance. By understanding the different types of NoSQL databases, you can choose the one that best fits your application's requirements.
In summary, document-based databases are ideal for applications that require flexibility and real-time analytics, key-value databases are ideal for applications that require high performance and scalability, column-family databases are ideal for applications that require scalability and high availability, and graph-based databases are ideal for applications that require complex data modeling and relationships.
Use cases for NoSQL databases
NoSQL databases are ideal for applications that require flexibility, scalability, and high performance. Some common use cases for NoSQL databases include:
- Real-time Analytics: NoSQL databases are ideal for real-time analytics applications that require fast and flexible data processing. With NoSQL databases, data can be stored in a semi-structured format, such as JSON or XML, allowing for easy data modeling and analysis. This makes them a great fit for applications that require real-time analytics, such as social media and e-commerce platforms.
- High-volume Transaction Processing: NoSQL databases are designed to handle high volumes of data and can scale horizontally to accommodate increased traffic. This makes them a great fit for high-volume transaction processing applications, such as financial services and e-commerce platforms.
- High-speed Content Delivery: NoSQL databases are optimized for fast read and write operations, making them ideal for high-speed content delivery applications, such as content management systems and media platforms.
Scenarios where NoSQL Databases are a Better Fit than Relational Databases
NoSQL databases are often a better fit than relational databases in scenarios that require:
- High Write Throughput: NoSQL databases are designed to handle high volumes of data and can scale horizontally to accommodate increased traffic. This makes them a great fit for applications that require high write throughput, such as social media platforms and financial services.
- Schema Flexibility: NoSQL databases do not enforce a fixed schema for data storage, allowing for greater flexibility in data modeling and simplified development processes. This makes them a great fit for applications that require schema flexibility, such as content management systems and real-time analytics.
- High Availability: NoSQL databases are designed to offer high availability, ensuring that data is accessible even in the event of hardware failures or network outages. This makes them a great fit for applications that require high availability, such as e-commerce platforms and financial services.
Factors to Consider when Choosing Between NoSQL and Relational Databases
When choosing between NoSQL and relational databases, it's important to consider several factors, including:
-
Search performance is one of the key strengths of Elasticsearch compared to traditional SQL databases. Elasticsearch is optimized for full-text search, which means that it is designed to quickly search through large amounts of text data.
In Elasticsearch, this is achieved through the use of an inverted index. An inverted index is a data structure that allows for very fast searching of text data. It works by creating an index of all the words in a set of documents, along with a list of which documents each word appears in. When a user searches for a specific term, Elasticsearch can quickly look up that term in the inverted index and return a list of documents that contain that term. This makes search performance much faster than traditional SQL databases, which typically use more complex query processing methods.
Elasticsearch also provides features such as relevance scoring, which can help to improve search performance even further. Relevance scoring allows Elasticsearch to return search results that are more relevant to the user's query, based on factors such as the frequency of the search term in the document, the length of the document, and other factors.
Overall, Elasticsearch's search performance is optimized for full-text search and can handle large amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data efficiently. SQL databases, on the other hand, may struggle with search performance when dealing with large amounts of text data, and may require more complex query processing to achieve the same results.
-
Scalability : another area where Elasticsearch outperforms SQL databases. Elasticsearch is designed to scale horizontally across multiple nodes, which allows it to handle large amounts of data and search queries more efficiently than a single SQL database server.
In Elasticsearch, data is divided into smaller segments, called shards, which can be distributed across multiple nodes in a cluster. When a search query is submitted, Elasticsearch can distribute the query across multiple shards in parallel, which can speed up search performance significantly. Additionally, Elasticsearch allows for the addition or removal of nodes in a cluster without any downtime or disruption, making it highly scalable.
SQL databases, on the other hand, are typically limited to a single server, which can be a bottleneck when dealing with large amounts of data or high search query volumes. Scaling SQL databases usually involves upgrading to more powerful hardware or partitioning the data across multiple servers, which can be complex and expensive.
Overall, Elasticsearch's scalability is a key advantage for applications that require large-scale search and analysis of unstructured or semi-structured data. By distributing data and search queries across multiple nodes, Elasticsearch can handle massive amounts of data and search requests more efficiently than SQL databases.
-
Flexibility : is another area where Elasticsearch outperforms SQL databases. Elasticsearch is designed to handle unstructured or semi-structured data, which means it can be used for a wide range of use cases, including full-text search, log analysis, and machine learning. Elasticsearch can also handle data in different formats, such as JSON, CSV, and XML.
In contrast, SQL databases are designed for structured data and have predefined schemas. SQL databases typically require data to be organized into tables with fixed columns and data types. This structure can be inflexible and can limit the types of data that can be stored and queried.
Elasticsearch's flexible data model allows for more complex queries and analysis, which can be especially useful for applications such as log analysis, where the data may not conform to a fixed schema. Additionally, Elasticsearch's support for different data formats and sources means that it can be easily integrated with other data sources and systems.
Overall, Elasticsearch's flexibility makes it a versatile tool for a wide range of use cases, from full-text search to machine learning, while SQL databases are typically limited to relational data management and querying.
-
Distributed computing: is a computing paradigm that involves multiple computers working together as a single system to perform a task. Elasticsearch is designed to be a distributed system, which means that it can perform data processing and analysis across multiple nodes in a cluster.
In Elasticsearch, data is divided into smaller segments, called shards, which can be distributed across multiple nodes in a cluster. When a query is submitted, Elasticsearch can distribute the query across multiple shards in parallel, which can speed up query performance significantly. Additionally, Elasticsearch allows for the addition or removal of nodes in a cluster without any downtime or disruption, making it highly scalable.
Distributed computing in Elasticsearch also enables fault tolerance. If a node fails or becomes unavailable, Elasticsearch can automatically reassign its shards to other nodes in the cluster, ensuring that data and search capabilities are not lost.
Overall, distributed computing in Elasticsearch enables fast query processing and scalability, as well as fault tolerance, making it an efficient and reliable solution for large-scale data processing and analysis. SQL databases, on the other hand, are typically designed for single-server deployments and may struggle to handle large amounts of data or high query volumes.
CAP theory
The CAP theorem is a concept in computer science that describes the limitations of distributed systems. Specifically, it describes the tradeoffs that must be made when designing distributed databases.
The CAP theorem states that a distributed system can only provide two of the following three guarantees at the same time:
- Consistency: All nodes in the system see the same data at the same time.
- Availability: Every request made to the system gets a response, without guarantee that it contains the most recent version of the information.
- Partition tolerance: The system continues to function even when network partitions occur, causing messages to be dropped or delayed between nodes.
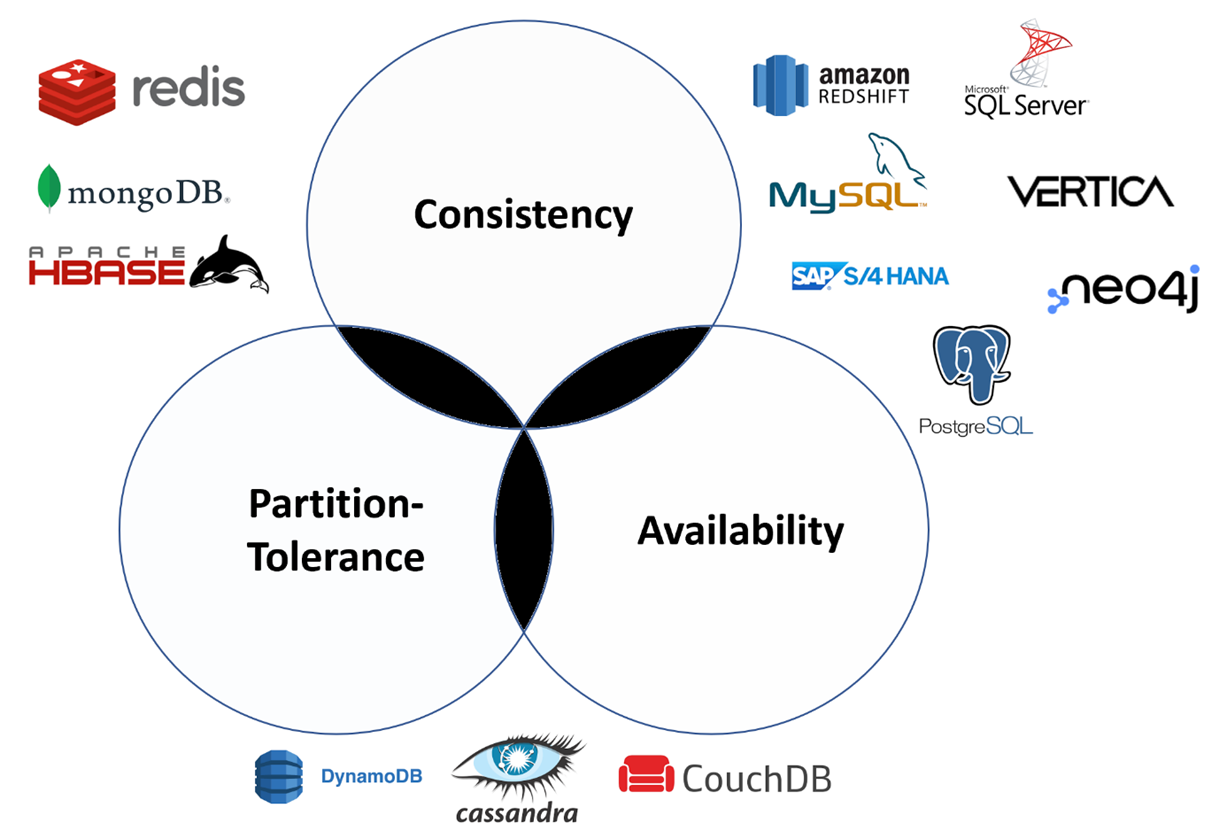 Source : https://data-science-blog.com/blog/2021/10/14/cap-theorem/
Source : https://data-science-blog.com/blog/2021/10/14/cap-theorem/
In other words, it is impossible to simultaneously achieve perfect consistency, availability, and partition tolerance in a distributed database system.
To put it simply, the CAP theorem states that a distributed database can be either consistent and partition tolerant (CP), available and partition tolerant (AP), or consistent and available (CA), but not all three at the same time.
Designers of distributed database systems need to make a trade-off between these three guarantees based on the specific needs of their application.